CBD (or cannabidiol) is one of the cannabinoids contained in the cannabis plant, along with THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). The many benefits of CBD relayed by the testimonies of consumers and by some scientific studies have made it, a molecule of weight recently. THC is classified as a narcotic substance because of its harmful psychotropic effects on health. However, CBD can be marketed in France. Lhemp plant from which it comes, must, however, respect a THC dosage lower than 0.2% (tolerance threshold in France). The number of cannabidiol shops is increasing. They offer many different and legal cannabic products (cannabis oil, capsules, hemp flowers, …). The large panel of consumers existing is thus satisfied.
Its relaxing virtues are widely appreciated. However, some weight-conscious individuals are still reluctant to deal with the cravings that cannabis use can bring. Indeed, who has never witnessed a late night party where the consumption of hemp is followed by irresistible cravings to eat foods rich in sugar and fat? If the effects of a CBD product would produce this craving, then we can understand these reluctances! However, some CBD shops are touting the benefits of cannabis as an excellent ally during a diet. It would optimize weight loss, it is to understand nothing! So, is CBD taken to lose weight or to gain weight?
Some biology notions about CBD
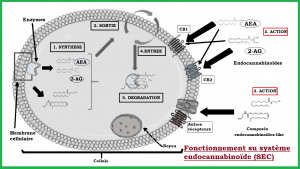
The endocannabinoid system (ECS)
The SEC is a communication system of the body governing various functions more or less complex to understand. It is composed of CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid membrane receptors, endogenous ligands (endocannabinoids) and enzymes responsible for the regulation of these molecules (1).
The endocannabinoids
These are the cannabinoids in our body. They are able to activate the CB1 and CB2 receptors of the endocannabinoid system. We find:
- l’
anandamide
(AEA) which binds essentially to the CB1 receptor. - 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) binds instead to the CB2 receptor.
Their production results from a stimulus. And, their actions are both local and temporary. Indeed, these molecules are rapidly degraded. CB1 and CB2 receptors are found throughout the body. Mainly in the nervous system. But also in the peripheral system (immune system, digestive system, liver, pancreas, adipose tissue, adrenal glands, cardiovascular system) (2).
The mitochondria
These are cellular organelles considered to be the “energy powerhouse” of our body. Their essential role is to transform into energy (ATP) the molecules present in the body (lipids, carbohydrates). Their functioning is also regulated by the endocannabinoid system.
Insulin
It is a vital hormone for the body. Secreted naturally by the pancreas, it is responsible for regulating the level of sugar (glucose) in the blood (blood sugar). In fact, it degrades it in order to make it available as a source of energy for the body’s cells. It also inhibits glucose production in the liver (central regulation). Finally, it plays an important role in protein metabolism, anabolism, and in fat storage (lipogenesis). Any dysfunction of insulin secretion has serious consequences on weight, but especially on health (diabetes, morbid obesity, …).
Adipose tissue
It is also commonly known as fat. It is made up of two types of cells: white and brown.
- The so-called white fat represents 95% of the body’s adipocytes. It can be a very important source of energy for the body. It must be present in reasonable proportion. On the other hand, found in excess, it has a deleterious impact on the functioning of the body. As a large hormone-producing machine (leptin, resistin, interleukin 6, …), a disproportionate presence of this white fat, also called “bad fat”, will have consequences on our body’s insulin management. It will be even more difficult to eliminate in the short and long term.
- The so-called brown fat also stores energy in lipid form. It consists of a larger number of mitochondria. As a result, the oxidation of fat and the burning of calories will be faster than with white fat to produce heat.
CBD has no affinity for CB1 and CB2 receptors. However, it produces indirect effects on the endocannabinoid system by acting on its enzymes. Therefore, it intervenes on the activation or inhibition of these receptors located everywhere. Cannabidiol would then be a privileged actor to ensure or restore the proper homeostatic functioning of this complex system.
CBD to lose weight?
Cs we have seen, the SEC is found throughout the body. Both in the brain (hypothalamus, …) and in peripheral tissues (liver, pancreas, …). Its action on appetite control, insulin production and mitochondrial homeostasis is therefore decisive for weight gain or loss.
A temporary or lasting alteration of the SEC can lead to physiological and psychological disorders responsible for obesity, diabetes, stress, and sleep disorders. CBD cannot claim to cure a disease like diabetes. However, its effects and broad spectrum of action could have real benefits on these disorders. Indeed, it can effectively regulate certain factors such as, for example, the storage of fat. The CBD appears therefore as a relevant help to lose weight.
The opinions and scientific studies on CBD to lose weight
CBD and fat storage
A poor quality diet has too much sugar and fat (carbohydrates and fats). It does not allow the mitochondria to produce as much energy as the nutrient supply they receive. This disproportion forces the liver to transform the remaining molecules into fat and to store them as adipose tissue under the skin.
According to a scientific study published in TheJournal of Neuroscience in February 2009, a consumption of CBD would allow a reinforcement of this mitochondrial activity by acting on the SEC. This would significantly limit the storage of bad fat (3). Here, the role of cannabidiol does not tend to make an individual lose weight. But, it prevents, in addition, a weight gain proportional to the quantity of food ingested.
CBD and weight loss
Prolonged consumption of foods rich in sugar has harmful consequences for health, such as hyperinsulinism (blood insulin levels outside the norm). This high concentration of insulin prevents the body from burning fat efficiently. This inexorably results in weight gain (among other things).
In 2013, research into the impact of cannabis on insulin levels in the body revealed:
- a 17% decrease of this hormone in subjects treated with hemp (4).
For these “test patients”, weight loss is therefore easier. As a result, cannabis, in the long term, could be an extremely beneficial treatment to limit the risks of obesity.
What is the best CBD product to lose weight?
All CBD products (flowers, resin, ..) have their specificity of use and effects.
CBD oils
are very concentrated legal cannabis consumables, easy to use and fast acting. They can be great allies in weight loss.
The full spectrum oil, in particular, allows a powerful surrounding effect (collaboration of the different molecules naturally present in hemp). Much more effective than the cannabidiol molecule alone (CBD isolate)!
Stress, CBD and weight
A stressed person can have a tendency to compensate a lack (psychological, emotional, …) by eating. By consuming CBD, she can see this need diminish, even cancel! 
Another effective way to keep the weight off!
In summary, does CBD make you lose weight?
The role of CBD on the functioning of the endocannabinoid system and its target tissues is still being studied. It is therefore impossible to determine with certainty all the effects of cannabidiol on weight loss or gain.
However, CBD has:
- anti-inflammatory actions
- an anti-oxidant action
- relaxing effects
- an impact on the homeostasis of the SEC
All of these benefits influence a number of factors that are directly or indirectly responsible for an individual’s weight gain or loss, depending on their physiology.
- “To the question, is it that CBD makes you lose weight?”, we can then answer: yes and no!
In fact, regular physical activity, a healthy diet and restful sleep are the keys to a healthy body weight on a daily basis. This lifestyle allows, executed in a more drastic way, to eliminate excess fat during a diet. Cannabidiol can also, in certain situations, intervene effectively on weight gain or loss. Indeed, it naturally helps the body to rebalance itself in the face of one or more disturbances.
Of the various CBD products on the market, the
cannabis oil
Of the various CBD products available, full spectrum organic grade CBD will respond more effectively than if the CBD molecule is isolated. In this way, it will bring the benefits of the entourage effect. The use of CBD does not make you lose weight miraculously. But, these numerous actions on the SEC make it a formidable ally for slimming!
FAQ : CBD and slimming
[sp_easyaccordion id=”10878″]
References:
- Fezza, F., Bari, M., Florio, R., Talamonti, E., Feole, M., and Maccarrone, M. (2014). Endocannabinoids, related compounds and their metabolic routes. Natioal Library of Medicine: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25347455/
- Sberna, A.-L., Degrace, P., and Vergès, B. (2016). Endocannabinoid system: effects on carbohydrate and also lipid metabolism. Medicine Of Metabolic Diseases. ScienceDirect: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1957255716301390
- Ryan, D., Drysdale, A. J., Lafourcade, C., Pertwee, R. G., & Platt, B. (2009). Cannabidiol targets mitochondria to regulate intracellular Ca2+ levels. Journal of Neuroscience: https://www.jneurosci.org/content/jneuro/29/7/2053.full.pdf
- Penner, E. A., Buettner, H., & Mittleman, M. A. (2013). The impact of marijuana use on glucose, insulin, and insulin resistance among US adults. The American journal of medicine: https://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(13)00200-3/fulltext